Jacqueline Baxter
Since the 1988 Education Act changed the educational landscape in England, heralding a new era of school self-management, the changes to English education have continued at a pace that is without precedent within other developed democracies. This has led many to describe it as ‘the lab of Europe.’ One of the most profound changes to take place has been the introduction of the academies programme in which schools, formerly overseen by Local Education Authorities (LEAs), have converted (or been coerced to convert following poor performance at an Ofsted inspection) to become semi-autonomous state subsidised schools in the form of Academies.
Operational drivers, such as the need to combine in order to cost effectively buy in services once provided by LEAs, combined with research that implies that inter school collaboration contributes positively to student progress, (Chapman et al 2009; NCTL, 2013), have also resulted in the creation of Academy Chains, Multi Academy Trusts and other less formal forms of collaboration between schools. As the literature on multi-level governance in the public and third sector reveals, (Foss et al, 2010), providing effective governance and accountability for complex collaborative organizations, which may also be widely geographically dispersed, creates a number of accountability challenges for organizations and the governance of such organizations.
Accountability past and present
Until 1988 the system of Educational accountability in England was focused on the LEA combined with an inspection system known as HMI – Her Majesty’s Inspectorate. The LEA combined their monitoring role with one which included both educational and pedagogic support with supply of back office services. Specialist advisers, very often subject specific, would work with schools and teachers to improve performance. HMI carried out regular inspections of schools, both general and thematic, in order to evaluate the quality of teaching and learning. This changed in 1992 when, prompted by John Major’s Citizen Charter, and accompanied by broader international trends premised on the rationale of public choice theory, Ofsted – The (then) Office for Standards in Education replaced the collegiality of HMI with a high stakes form of inspection and regulation. The system also introduced use of school league tables to evaluate the quality of schools. This too formed part of a broader educational trend that has become known as ‘Governing by numbers’.
A changing system
The introduction of the academies programme under the Blair administration, originally offered freedom from LEA control (both financial and curricular), for failing schools in the London region. The programme was so successful that it was extended to other schools, at first on a meritocratic basis- only successful schools could apply to convert – but following the Academies Act in 2010, the programme was intensified and schools were offered substantial financial incentives to convert. Over time this began to radically change the educational landscape as more schools were either incentivised, or in the case of failing schools, were coerced into conversion, following unfavourable judgements by Ofsted. Ofsted’s remit was increased to incorporate inspection of whole Education Authorities (LEAs), a good number of which, were found to be failing.
This also coincided with a dramatic reduction in LEA funding, justified by austerity policies, which effectively undermined their capacity to offer its former wide range of services to schools remaining under LEA control. Although, in response to widespread protest, the government subsequently did a u-turn in terms of turning the plans into legislation, (Whittaker, 2016); there is little doubt that, in practice, they have not deviated from their plans and the number of schools joining MATs continues to rise. In November 2017 there were over 20,100 state funded schools in England, of these 6100 were academies with 1668 standalone academies and 4,432 MATs. MATs may have anything from 2 to over 100 schools.
The accountability maze
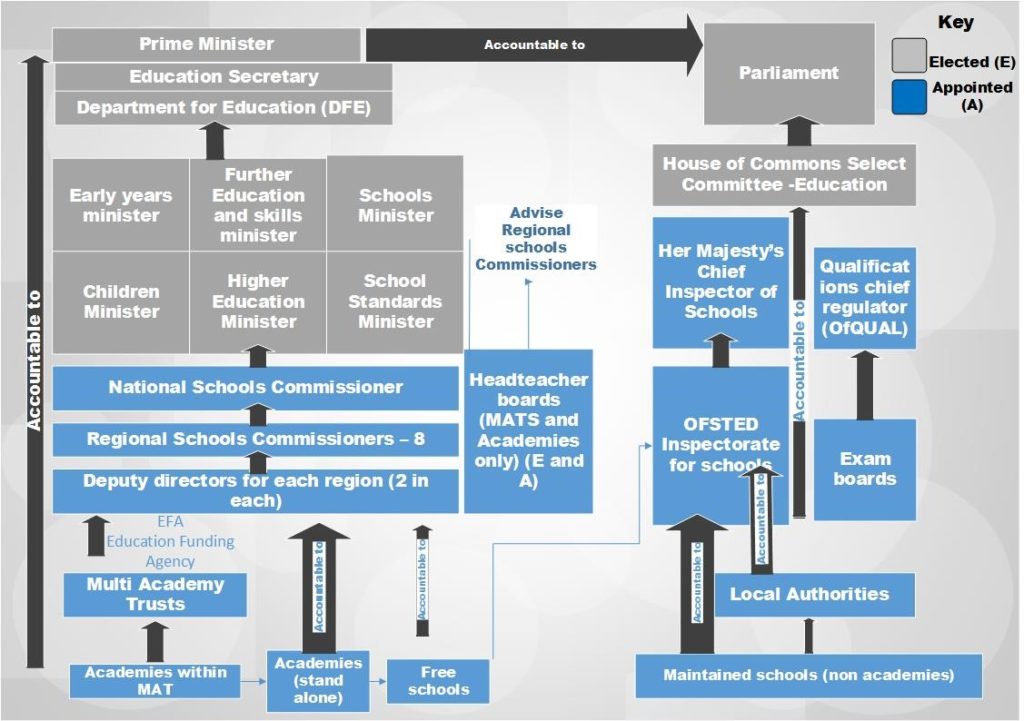
Since then the system of accountability has become increasingly complex, diluted and fragmented as figure 1 illustrates.
MATs are regulated financially by the EFA (Education funding Agency), their expansion is overseen by 8 regional schools commissioners and their schools are inspected by Ofsted. However, Ofsted are not permitted to inspect MATs as a whole. This means that they cannot inspect /monitor boards at the apex of the organization- trust boards and their CEOs. In addition to this, their regions (and regional directorates) do not coincide with the RSC regions, thus, there is little joined up approach between them. This has been widely criticised by both the Education Select Committee (Parliament, 2017), and in numerous press reports, particularly in light of the increasing number of MAT failures.
The pressure on good MATs to expand is enormous. Regional Schools Commissioners are under a great deal of pressure to re-broker (find a new sponsor) for poor schools, and as LEAs are increasingly unable to cope with the many demands placed on them, schools turn to MATS for support (J. Baxter, 2018). In addition to this, due to the complex multi-level governance structures within MATs, they are having to work very hard and creatively to ensure that they are in touch with their school communities (Baxter, 2018). A recent report by the Education Select Committee questioned the rationale behind MAT expansion in light of the numerous MAT failures that have recently been in the press (see Baxter, 2018).
The pressure of accountability emanates from a number of sources: from the high stakes inspection system that considers schools within MATs in a fragmented way; Regional Schools Commissioners, keen to add failing schools to MAT portfolios and from the Education Funding Agency, who monitor MAT finances. Unfortunately, the unrelenting pressures on MATs to prove that their model is the best one, is a key pressure within the highly marketized system of English education. And leading to lack of collaboration between MATs, as one MAT CEO put it: ‘MATs don’t share, they compete against each other.’
Managing and governing collaborative organizations is no mean feat, as the literature on collaborative advantage illustrates (see for example, Vangen, Hayes, & Cornforth, 2015). Even when all of the collaborating organizations are keen for it to work, the challenges of factors such as: the creation of a coherent organizational identity; ensuring that the tension between conformity and autonomy of organizations within the group is well managed, and, ensuring that internal as well as external accountability is clear and productive- i.e. that it works towards the organizational mission and not against it; are demanding of the most able management and leadership teams.
The English system of education after 30 years of government tinkering, is in a very difficult place. Support and accountability systems provided by the LEA are in many cases either gone or so deprived of funding, due to cuts and academy conversions that they have little or no capacity to support or provide local accountability. Ofsted, for so many years the schools’ ‘watchdog’, no longer has the capacity or the skills to inspect these new structures. The vast cash injection it would take in order to train up inspectors to oversee MAT boards with budgets of millions, is unlikely to be forthcoming under present government policy.
Where do we go from here?
So where do we go from here? Well a good place to start would be to join up the existing accountability mechanisms so that Ofsted’s educational expertise , the EFA’s financial oversight and Regional Commissioner’s growing local knowledge , could provide a 360 picture of, not only what is going on in MATs but equally, provide some sense of impending and serious failings.
Any such system should also have some way of measuring exactly how and to what extent these large organizations are serving the communities in which they are situated. Only then could the public be reassured that we have anything remotely resembling a democratic system of Education in England.
References:
Baxter, J. (2018). Engaging with local communities: the challenge of board engagement with school communities in multi- academy trusts. Under review.
Baxter, J. (2018). MAT Accountability : Challenges and Opportunities for Inspectors and school Leaders. . Keynote speech presented at the ‘Raising Standards through MAT inspection’ Conference ,19th June. London, Holborn .
Chapman, C., Collins, A., Sammons, P., Armstrong, P., & Muijs, D. (2009). The impact of federations on student outcomes.
Foss, N. J., Husted, K., & Michailova, S. (2010). Governing knowledge sharing in organizations: Levels of analysis, governance mechanisms, and research directions. Journal of Management Studies, 47(3), 455-482.
NCTL. (2013). Governance in Multi Academy Trusts. London: National College for Teaching and Leadership.
Parliament, U. (2017). Multi-Academy Trusts: Seventh Report of Sesssion 2016-17. In H. o. C. E. Committee (Ed.). London: House of Commons .
Vangen, S., Hayes, J. P., & Cornforth, C. (2015). Governing cross-sector, inter-organizational collaborations. Public Management Review, 17(9), 1237-1260.
Jacqueline Baxter is Senior Lecturer /Associate Professor in Public Policy and Management , based in The Department of Public Leadership and Social Enterprise at the Open University Business school. Her research interests lie in the area of public service governance, accountability and trust. This article is part of a current funded project. She is Editor in Chief for the Sage publication Management in Education, and tweets at @drjacquebaxter. The author gratefully acknowledges funding received by The British Academy Lever Hulme Trust grant number SG161312